MYTH:
Kangaroos are farmed.
TRUTH:
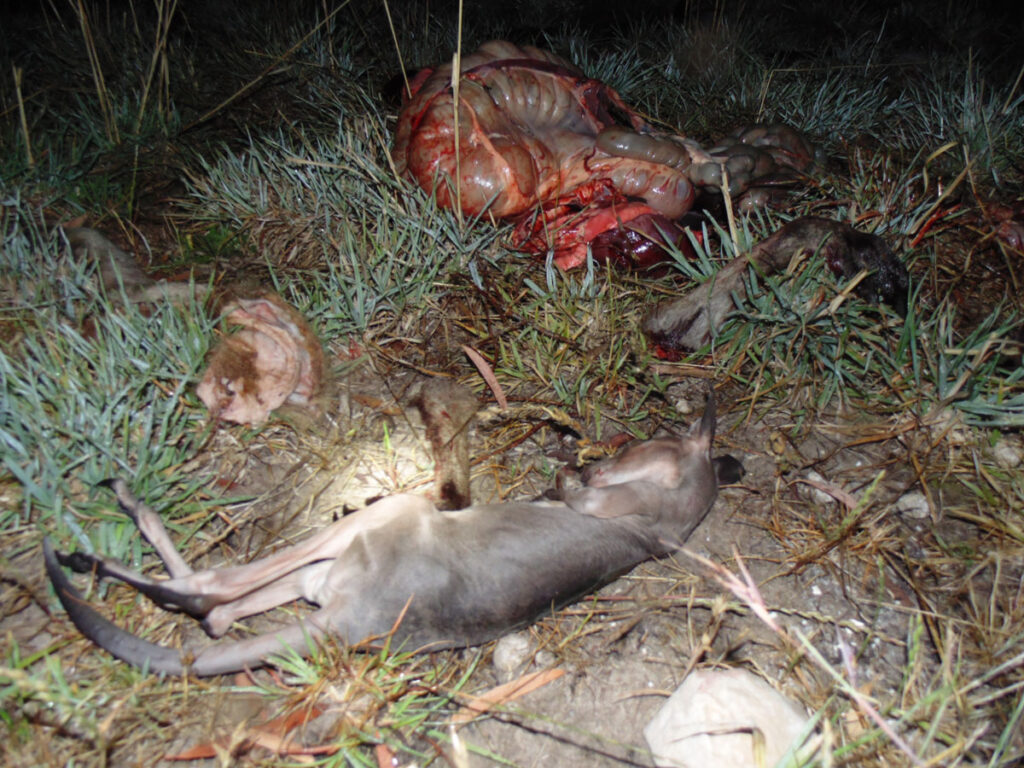
Kangaroos are wild animals. They are not farmed. Every night in Australia, thousands of wild kangaroos are hunted and killed for their meat and skins. Dependent joeys are bludgeoned to death. Dependent young at foot often flee in fright and die slow painful deaths due to starvation, exposure or predation.

MYTH:
Kangaroos are overabundant.
TRUTH:
Kangaroo numbers fluctuate depending on conditions. Australia has been in drought for 13 out of the last 20 years. Research concludes that during drought kangaroo numbers decline by up to 65%. In 2001, the Australian government estimated a kangaroo population of 57 million. Five years later, during the Millennium Drought, kangaroo numbers declined to 24 million. Right now, due to drought, bushfires, habitat loss, disease, illegal and legal hunting, car accidents, fences and animal abuse, kangaroo numbers are less than 20 million. Kangaroos are a rare sight in the Australian landscape.
MYTH:
Kangaroos are in plague proportions.
TRUTH:
A plague is biologically impossible because kangaroos are slow-growing with low reproductive rates and normal 73% juvenile mortality rates with 50% taken by foxes (Banks et al 2000)..Contemporary science agrees that the maximum population growth rate is 10% (Arnold 1991; Bilton & Croft 2004). A female kangaroo, aged 2 to 3 years old, will have one joey a year. A joey stays in the pouch for approximately 11 months, which means a female kangaroo can only have one joey a year. Averaged across species, it takes an average of 18 months for a kangaroo joey to become fully independent of its mother (eg Poole 1975; Jackson; Staker,L; Dawson 1995) effectively producing just one joey to independence per annum. Mortality rates for joeys are high, around 73% during good times and 100% during bad times. Kangaroos don’t breed during drought because there isn’t enough food.

MYTH:
Kangaroos need to be culled.
TRUTH:
Australia has cleared 80% of land for agriculture – crops and livestock. Australia grazes 69 million sheep, 27 million cattle and 2.5 million goats. White settlers cleared the land of trees and kangaroos so they could grow crops and graze livestock. Kangaroos were shot for simply being in the way. This tradition continues today. Too many farmers maintain the attitude of white settlers: a kangaroo found on farmland must be shot. Kangaroos are also shot for living on land earmarked for development.
We live in a world where no animal is allowed to live unless it has value to humans. Unfortunately, Australian governments see kangaroos as a resource for a commercial industry. Kangaroos are tolerated so that 3 million wild kangaroos can be killed each year for their meat and skins. The only reason Australia culls kangaroos is because a commercial industry needs the dead bodies to supply domestic and overseas markets.

MYTH:
The commercial killing of millions of kangaroos every year is sustainable.
TRUTH:
During drought kangaroo numbers are known to decline by up to 65%. In 2019-2020, unprecedented bushfires in Australia killed an estimated 3 billion animals. No one knows how many kangaroos were killed. Yet, the commercial killing of kangaroos continues.
Australian governments quote science to justify the killing of kangaroos. One of the most quoted reports is Kangaroo Management Options in the Murray-Darling Basin (Hacker et al, 2004). This report states that populations below 2 kangaroos per square kilometre would generally be considered at risk of extinction. Every state in Australia kills kangaroo populations considered at risk of extinction. In Tibooburra, a region of New South Wales, grey kangaroos at risk of extinction with a density of 0.9 kangaroos per square kilometre are killed at a rate of 14%. In Charters, a region of Queensland, red kangaroos at risk of extinction with a density of 0.28 kangaroos per square kilometre are killed at a rate of 10%. In Kingoonya, a region of South Australia, grey kangaroos at risk of extinction with a density of 0.18 kangaroos per square kilometre are killed at a rate of 12%. There are dozens of examples of kangaroos at risk of extinction being killed for a commercial industry at rates of 10% to 17%.
The worse case of kangaroos being hunted to extinction is in the mid-north of South Australia, where a total population of less than 5,000 red kangaroos is killed at 17% or 1,500 per year. Three years ago, the total population was approximately 32,000 red kangaroos. Now there are less than 5,000 and hunters can killed up to 1,500 of the 5,000 in 2020.
The killing of kangaroos is driven by market demand, not sustainability.

MYTH:
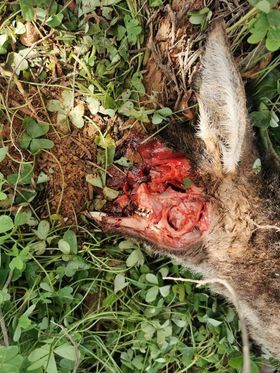
The shooting of kangaroos is humane because kangaroos are shot in the head and die instantly.
TRUTH:
“An independent assessment of compliance with the Code, carried out by Animal Liberation NSW between 2005 and 2008, has identified an average of 40% of kangaroos per chiller in 24 chillers throughout New South Wales and Queensland were neck shot. Neck shot kangaroos may suffer a painful death, which is a clear transgression of
humane practices and the Code guidelines.” (A Shot in the Dark: A Report on Kangaroo Harvesting by Dror Ben-Ami, PhD, 2009)
“Cole has come home with 16 roos, a disappointing tally. He shot two more, but couldn’t find them to retrieve. He’d climbed onto the tray, looked through the monocle that uses thermal imaging to detect body heat, but no good.” (From dusk to dawn: A night in the life of a roo shooter, ABC News, 2018)
No one knows how many kangaroos are injured and disappear into the bush to die slow, painful deaths. Injured kangaroos are never recorded or acknowledged by the commercial industry.

MYTH:
Kangaroo numbers have increased since European settlement.
TRUTH:
“The conventional wisdom is that kangaroo (Macropus spp.) numbers have increased in Australia since European settlement due to cessation of predation by Aborigines and dingoes (Cpnis lupus dingo), as well as increased availability of water. The historical record shows that at the time of first European contact the kangaroo was numerous and abundant over the continent and Tasmania.
“Water supplies were largely unimproved by 1860 when Australia de-pastured domestic livestock equivalent to 110 million kangaroos. In 1880 when there were 240 million kangaroo-equivalents, water supplies had been upgraded only in closely settled areas. It seems probable that at the time of settlement kangaroo numbers exceeded the present population at least threefold.
“EXAMINATION of the historical record reveals that kangaroos (Macropus spp.) were widespread in their distribution at the time of European exploration and settlement of Australia and are usually described as being numerous or abundant.
“The population was probably of the order of one to two hundred million.” (Red Plague Grey Plague: The Kangaroo Myths and Legends, Joe Auty, 2004)
MYTH:
Kangaroo numbers have increased since European settlement due to increased availability of water.
TRUTH:
“The interpretation that these numerous water sources are necessary to sustain the kangaroo population is a falsehood generated by looking at the landscape though the eyes of a livestock manager. This viewpoint started with the very first explorers into the inland.
“Kangaroos have a long narrow muzzle and equally long tongue with which they lap water making small ephemeral sources accessible (Fig. 8). If surface water is not available kangaroos will dig soaks in creeks gaining access to further water that is not available to livestock. Furthermore, all the species of kangaroos need much less water than livestock. Graziers normally budget 10 litres per day for sheep with this potentially doubling in a hot dry summer. The water turnover in summer is around 1 litre tor a 25 kg red kangaroo or euro and 1 75 litres for a 25 kg eastern grey kangaroo. Not all of this is required from drinking as water taken in with plant matter and created by oxidation of foodstuffs both add to the water budget.
“Thus kangaroos are relatively miserly drinkers compared lo livestock and certainly people. They lap with a long and narrow tongue and do not suck water. They can exploit water sources that are small and shallow, which are insufficient for livestock.
“Furthermore, my observations made during a study of drinking behaviour (Croft 1985) revealed that they will readily lap muddy and algae infested water that is unacceptable to sheep. For kangaroos, light rainfalls across the hotter months will maintain adequate ephemeral water sources in the many catchments from claypans and gilgais to swamps and lakes. Many of these have been silted up by the much accelerated erosion introduced by livestock and overstocking (Fanning 1984: Condon 2002). Large water holes have been replaced but not necessarily supplemented by earthen tanks. Many of the latter lie on top of old springs or simply create deep holes in existing swamps. Kangaroos may have expanded the‹r range into areas of central Australia where artesian bores have provided water (Newsome 1980) but equally much well-watered habitat has been lost to irrigated horticulture and crops along inland rivers.” (The future of kangaroos – Going, going, Gone? Croft 2005)
Millions of creeks used to run through Australia. Most of them are now dry due to large dams and reservoirs. While farmers have introduced small water points for livestock, most of the creeks and rivers are no longer available to kangaroos due to dams, reservoirs and irrigation. However, research indicates that kangaroos require very little water. During drought, kangaroos die from lack of food, not lack of water.

MYTH:
Kangaroo numbers have increased since European settlement due to a lack of predator.
TRUTH:
Kangaroos have many predators.
“Dingoes that live in temperate and sub-tropical eastern Australia more commonly dine on medium-sized and large mammals, including bandicoots, possums, wallabies and kangaroos. For instance, one study from the Blue Mountains found that large mammals occurred in more than 80% of dingo scats, including swamp wallabies in 29% of scats and wombats in 11%.” (Doherty, 2018)
Feral and domestic dogs also kill kangaroos. Foxes kill 50% of all joeys born (Banks, 2000). Between 80 and 90% of a wedge-tailed eagle’s diet is made up of ground-dwelling animals, including rabbits, wallabies and small kangaroos.
Humans kill approximately 4 million kangaroos every year, mainly through the commercial harvest of kangaroos. Other reasons for killing kangaroos are farmers killing kangaroos for being on their property, developers killing kangaroos for being on their property, drivers hitting kangaroos, kangaroos getting caught in fences and animal abuse.
During drought, kangaroo numbers plummet by up to 65%. Kangaroos don’t breed during drought. Every year, bushfires kill unknown numbers of kangaroos.
MYTH:
Kangaroos damage the environment.
TRUTH:
“Kangaroos aerate soils, top graze dry native grasses thus promoting regenerative growth, and reducing the risk of bushfires. They are essential in seed dispersal, have soft padded feet, and don’t have a water-focused grazing pattern.
“Kangaroo poo is THE best natural fertiliser on the planet, ask any sustainable food producer.
“Research shows that mixed grazing, at sustainable stocking rates between cattle and kangaroos or sheep and kangaroos, is more productive and ecologically sound as kangaroos counteract the destructive grazing patterns of introduced hard-hooved livestock.
“Kangaroos are a keystone species upon which various other indigenous species of flora and fauna depend for their own survival.” (Aunty Ro Mudyin Godwin, 2019)
“The soft padded feet and long tail of the kangaroo are essential for the ecological health of the land as regenerators of native grasses.” (D Ramp)

MYTH:
Kangaroos compete with livestock.
TRUTH:
Let’s put the above statement into context. The total number of grazed livestock in Australia is approximately 100 million. Kangaroo numbers have crashed due to drought and bushfires. The total number of kangaroos in Australia is less than 20 million.
In 2000, two studies (Pople and McLeod, Olsen and Braysher) concluded that competition between sheep and kangaroos seldom occurs because food is not limited or food choices and feeding sites differ.
“Kangaroos and sheep have not been demonstrated to compete to any significant degree because of differences in diet and spatial use of pastures, except under very poor forage conditions. Grigg (2002) cast serious doubt upon the common assumption that kangaroos have 70% of the food requirements of sheep (a DSE of 0.7), proposing that the correct figure may be 20% (a DSE of 0.2). Dawson and Munn (in press) have since improved the estimate, to 0.48 (48%) using captive animals. This decreases any likelihood of competition and economic loss associated with grazing by kangaroos, and suggests that predictions and estimates based on the old DSE estimates exaggerate kangaroo impacts.” (Penny Olsen & Tim Low, 2006).
MYTH:
Kangaroos cause $90 million damage to crops, fences and equipment.
TRUTH:
This myth is common but little research has been done to prove or disprove this myth.
“Indeed, there is little convincing evidence of substantial damage by kangaroos to crops, pastoral production or rangelands, except in a few localized areas.” (Penny Olsen & Tim Low, 2006)
Table 2.
“Kangaroos generally keep within 100 m or so of the bush that they use for shelter, so crop damage is usually restricted to this zone of the paddock. Measurements were made of crop losses from kangaroos in crops bordering the Tutanning Reserve near Pingelly. These averaged 1 to 2 per cent of paddock yield. Similar results were obtained for crops around the Durakoppin Reserve at Kellerberrin. In some situations losses will be higher, but more than 95 per cent of crops in the wheatbelt are never visited by kangaroos.” (Dr Graham Arnold, 1990)
“Pests is an emotive word. It conjures up visions of animals destroying crops. I can think of no situations where this is likely to be true for kangaroos.” (Dr Graham Arnold, CSIRO)
“Sometimes damage is attributed to kangaroos but the real perpetrator is another animal or even insects. In the Kinchega area, the NSW NPWS first thought that damage to vegetation during the 1982-83 drought was caused by kangaroos, but further investigation indicated that pasture insects were responsible. The Queensland NPWS has also drawn attention to the role of native insects, particularly termites, in pasture losses. Other animals such as pigs, mice, rabbits, hares, donkeys, goats, wombats and emus may also be responsible for damage to pasture.” (Senate Select Committee on Animal Welfare, 1988)